Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links. This means that at no cost to you, we may earn a small commission for qualifying purchases.
Last Updated on December 24, 2021
Electric Generators are useful machines that are excellent tools when it comes to producing usable mechanical energy. They are versatile and can be used in many different situations, be it work-related or personal use.
The key to using an electric generator properly and to its fullest potential is to have all the information. These tools have the potential to do a lot for you, but only if you know how to use it. Take a look at our full guide on generators to learn about the different types and ways you can use them.
Contents
What is an Electric Generator?
A generator is a machine designed to convert mechanical power into electric current. Generators are most often used in situations where electric current is not readily available.
While in most cases you could use electricity by plugging your item into an outlet, sometimes there aren’t any outlets available. A generator lets your product your own electricity using battery power or fuel.
What Kind of Electric Generators Are There?
There are several different kinds of generators in existence today. They each have their own benefits as well as ideal usage situations. Let’s take a look at some of the different types.
Portable/Recreational Generators
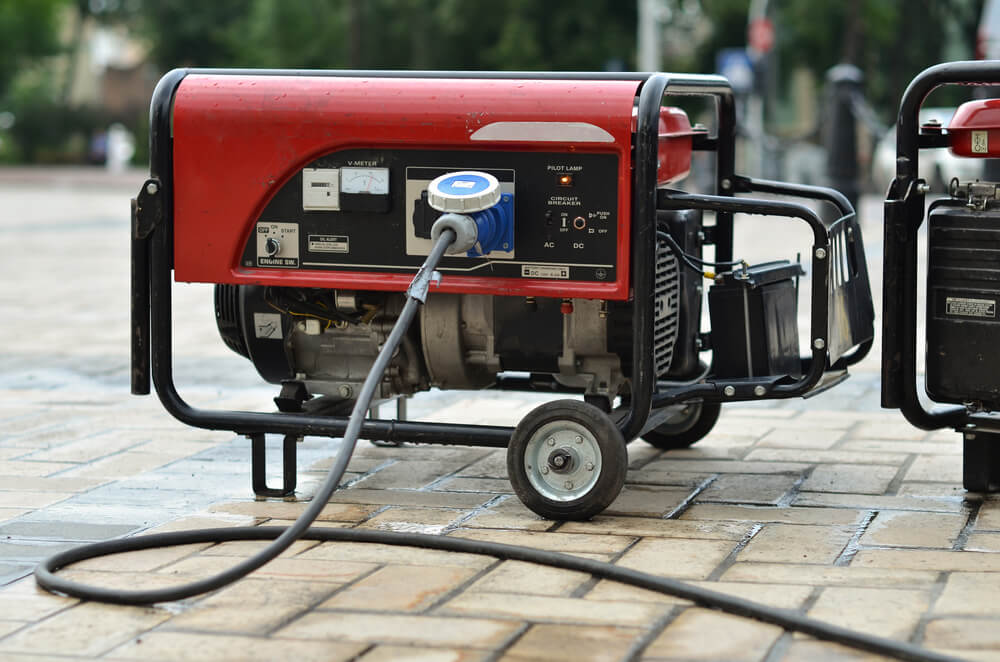

Portable generators are the smallest kinds of generators you can find. They are most often used recreationally for things like powering RVs or using on camping trips.
Portable residential generators are also used within the home for cases of emergencies. They are excellent solutions to random power outages due to natural disasters like storms and strong winds. Many homeowners like to use these smaller generators to power things like refrigerators, lights, pumps, and furnaces during outages.
Some portable generators can power most appliances in a home, while others are more useful for charges devices and keeping the lights on.
Portable Construction and Industrial Generators
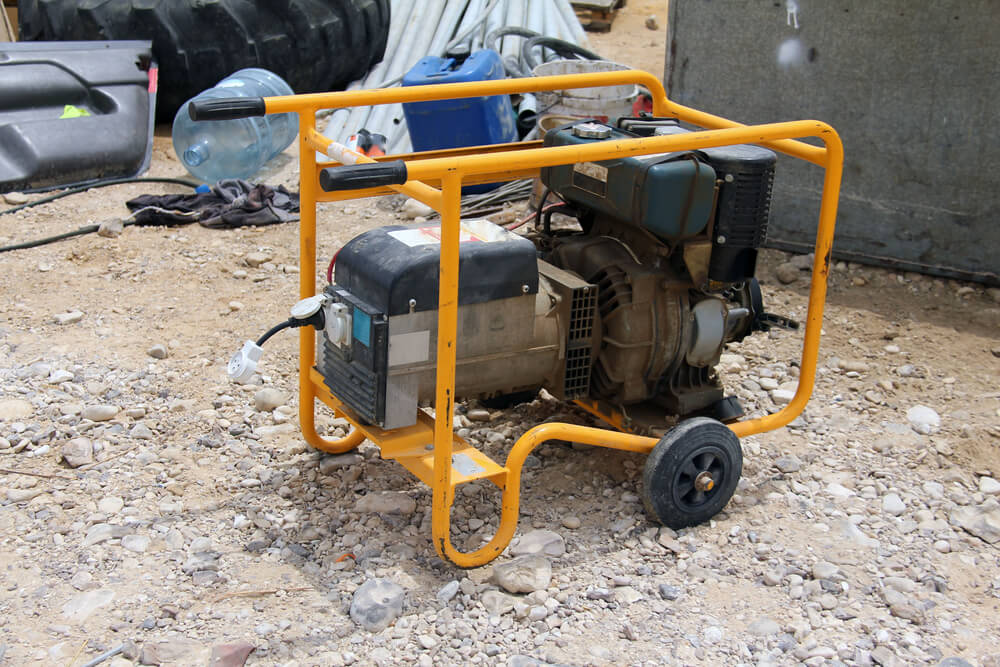

While it’s true that portable generators are cross-functional between residential and industrial use, some portable generators are just made to better handle the more demanding needs of construction. These generators give you excellent efficiency and power on the job site.
Many of them feature upgraded diesel engines that are designed to take on heavier loads, while other portable generators use traditional gas tanks. Construction and industrial generators also usually have high-cycle power for power tools.
Vehicle Mounted Generators :
The name is pretty self-explanatory: vehicle-mounted generators are mounted on vehicles. They’re often used in cases of emergency as well as construction us, mining applications, and field use.
Standby Generators
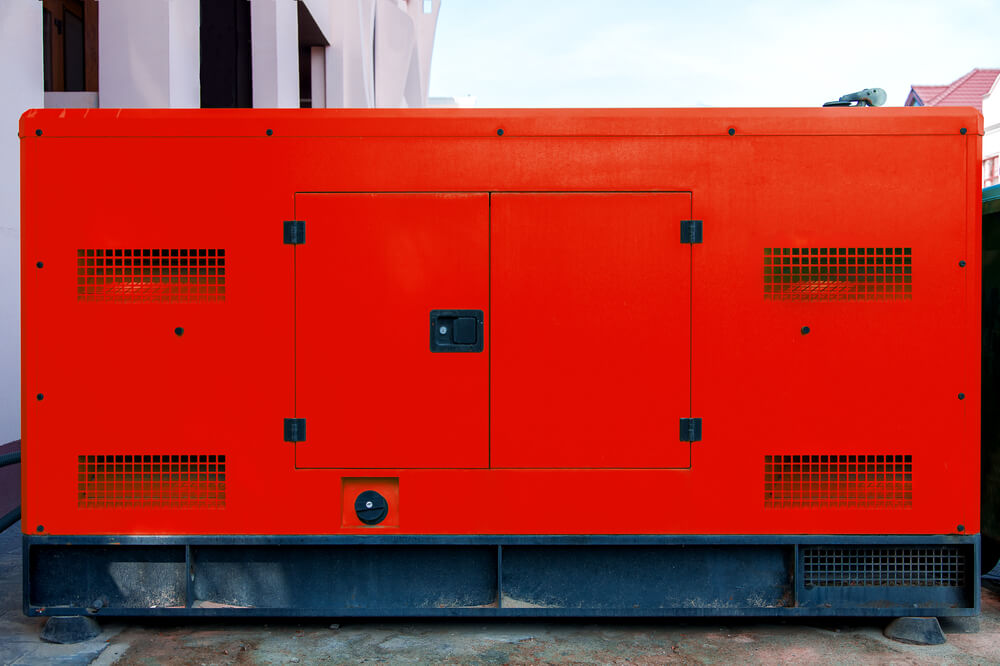

Standby generators are large generators attached to businesses or residential buildings to be used as backup power. They are typically designed to automatically take on the job of powering a building when the electricity fails.
They’re very strong, as they need to power entire buildings, but they are also sometimes used in industrial or agricultural situations.
PTO Generators
PTO generators are highly portable machines that are used for mobile applications, like tractors. They are most often used in cases of yard or farm work since they are highly portable on mobile machines.
There are several other types of generators, but there are just a few of the main types.
How Do Generators Work?
We already know that a generator converts mechanical energy obtained from an external energy source into electrical energy. That’s easy enough to say, but do we truly understand what that means?
Contrary to what its name may imply, a generator does not actually create its own electrical energy. Modern-day generators work on the principle of electromagnetic field. The machine is designed to take mechanical energy supplied to it and use it to establish the movement of electric charges. That is where the power output comes from. Micheal Faraday discovered that the above flow of electric charges could be induced by moving an electrical conductor, such as a wire that contains electric charges, in a magnetic field. This movement of the magnetic field creates a voltage difference between the two ends of the wire or electrical conductor
To force the movement of electric charges, every generator needs an engine—just like your car. And similar to your car, the engine needs to be fueled by something.
There are a few different fuel types that generators use:
- Gasoline
- Propane
- Natural Gas
- Diesel
- Batteries
Each of these fuel sources has its benefits and downfalls. For example, diesel types of generators are more efficient and lasts longer, but it’s much more expensive than gasoline and natural gas types of generators.
For larger, more industrial-type generators, you’ll most often see diesel or propane being used. Smaller generators tend to run on gasoline or batteries.
Batteries vs. Fuel
Many smaller electricity generators run on battery power, while some use fuel with the option to include a battery. There’s no right or wrong answer, but they both have upsides and downfalls.
Batteries are great because they are rechargeable. Unlike a fuel source, you only have to make one purchase for continued use. When your generator runs out of power, you simply plug it in and charge it up.
That sounds like a great deal, so why wouldn’t everyone just use batteries? Well, the downside to batteries is multifaceted. For one, their charge does not last as long as a full tank of fuel lasts. The second disadvantage is that battery-operated generators are usually more expensive than fuel-run machines.
Thirdly, it takes a long time to fully recharge a battery. In an emergency where you’ve lost long-term power in your home, not only do you not have the resources to recharge your battery, but you don’t exactly have the time either—whereas, with fuel, you can just refill the tank and start it up again.
Finally, battery-operated generators usually don’t supply as much power as fuel operated engines.
Fuel seems like the obvious choice now, although fuel also has a few downsides. The biggest annoyance about fuel is that you have to keep buying it over and over again to refill. And, should you forget to stock up, you may find yourself in an emergency situation with a generator, but no fuel.
Depending on your fuel source— natural gas, diesel, propane—it can get expensive. However, if you’re main use is as a backup energy source, it’s probably worth it to have a few gallons handy at all times. You’ll be happy when you’re not freezing during a snowstorm blackout.
Common Uses Of Electric Generators
You can learn everything you need to know about electricity generators and how they work, but how do they benefit you or your business? Realistically, electric generators have some very practical uses and are pretty common in homes and commercial buildings today.
Backup Power
Backup power is probably the number one reason that folks purchase electric generators. Power outages happen for several reasons: hurricanes, flooding, construction, high winds—you name it; it can affect your power.
Some people may be content to sit and tough it out until the electric company figures out the issue and solves it, but others prefer a more proactive approach. Sometimes there’s no telling how long an outage will last. Your house can start to get cold if it’s wintertime.
You can also lose hundreds of dollars in groceries without electricity to your refrigerator. Families with young children can find comfort in just being able to turn on a light.
Backup generators—whether you’re using a whole house generator or a small, portable generator—can give you enough power to last you until the issue is straightened out and this type of generator is the best generator during a power outage.
Standby Power
Standby generators, as we discussed earlier, are very common in public buildings and businesses. Power outages put everything on hold. Smart business owners should invest in standby generators to keep their buildings up and running, even when there’s no electricity.
Publicly and privately-owned properties often invest in standby power. Buildings like hotels, dorm rooms, campus halls, schools, and apartment buildings are likely to have standby generators because they serve a large number of people on a regular basis.
Large Events
Concerts, festivals, weddings—these are all fun events that require a lot of power. Events in well-populated areas will likely have access to electricity as well as standby power, but some of these instances occur outside of main power grids and in rural areas.
Generators are great for powering such events, or even just serving as a backup should something happen to the main source. They can be used for lighting, speakers, catering equipment, and DJ equipment.
Camping and Traveling
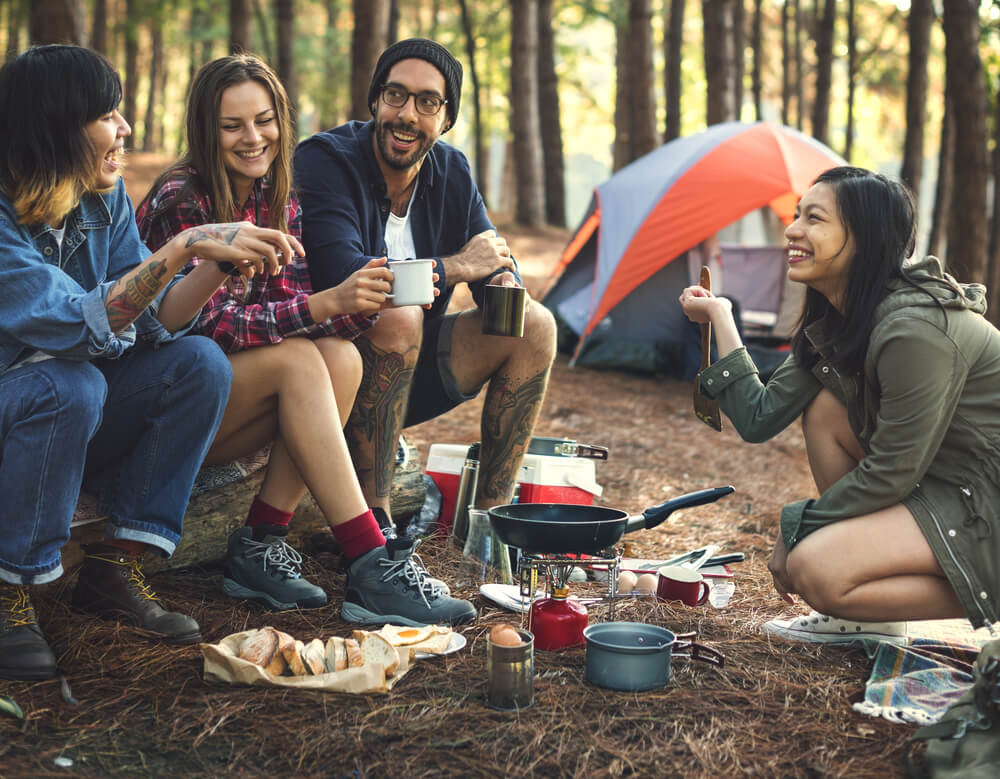

Outdoor enthusiasts can still enjoy nature while bringing a little bit of comfort with them. Portable generators (especially inverter generators) are perfect for camping trips and outdoor vacations. With even a small generator, you can bring along your phone and devices as well as additional lighting and space heaters.
You could also power things like projectors to watch movies or speakers for a little campfire music. Portable stoves and microwaves are even options if you have a reliable generator.
Stronger portable generators are very commonly used to power RV and trailers. If you’re camping in a trailer outside of a trailer park, you are going to need a power source to use your home on wheels.
Sporting Events
Did you know that premier league stadiums require the use of a standby generator? A standby generator could mean the difference between a great game and it being canceled mid-quarter.
Electric generators can be used to ensure properly functioning floodlighting and electricity for the fans. Without lighting and power, the players can’t see, the fans can’t enjoy, and they’re certainly won’t be any hotdogs for sale.
Generator Maintenance and Tips
Standby Generator is not cheap. There aren’t like other tools that you can go out and replace the day it breaks or stops working. With an investment like this, it’s important to properly maintain your machine so you can get the most possible years of use out of it.
Don’t Ignore the Wattage
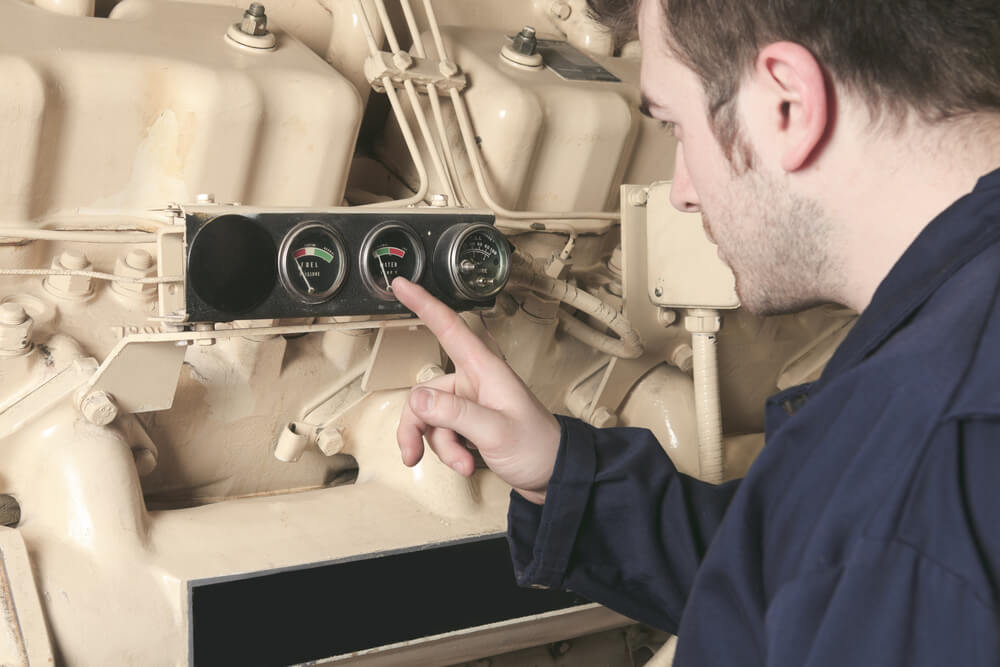

When you purchase or use a generator of any kind, the first thing you’ll likely look for is the wattage. Generators will list two different wattage numbers for you. The first is the rated or running wattage, and the second is the starting or maximum wattage.
The most important of these two numbers is the running wattage. This will be the lower number and describes the power your generator will offer on an extended basis.
The starting wattage tells you how much power a generator can put out within the first few seconds. This little extra boost helps your generator get other motors started. However, once you get them started, the wattage will drop to its running wattage.
Trying to run something based off of the starting wattage will certainly burn out your generator.
Oil and Filter Changes
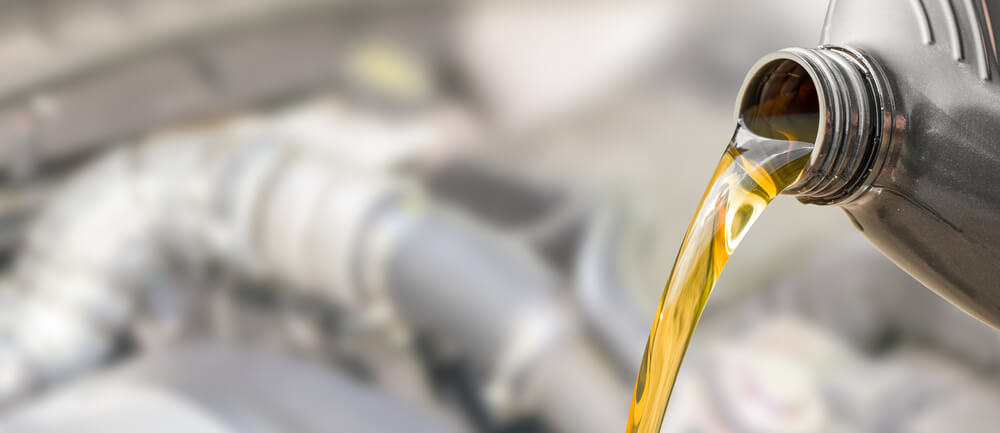

It’s very important to stay consistent with oil changes and filter replacements. Just like your car needs a regular oil change to keep your engine running, so does a generator. Every generator is different in terms of the exact amount of time between changes, so make sure you determine these numbers and stock up before you start using a generator.
Keep a Close Eye on Fuel Levels
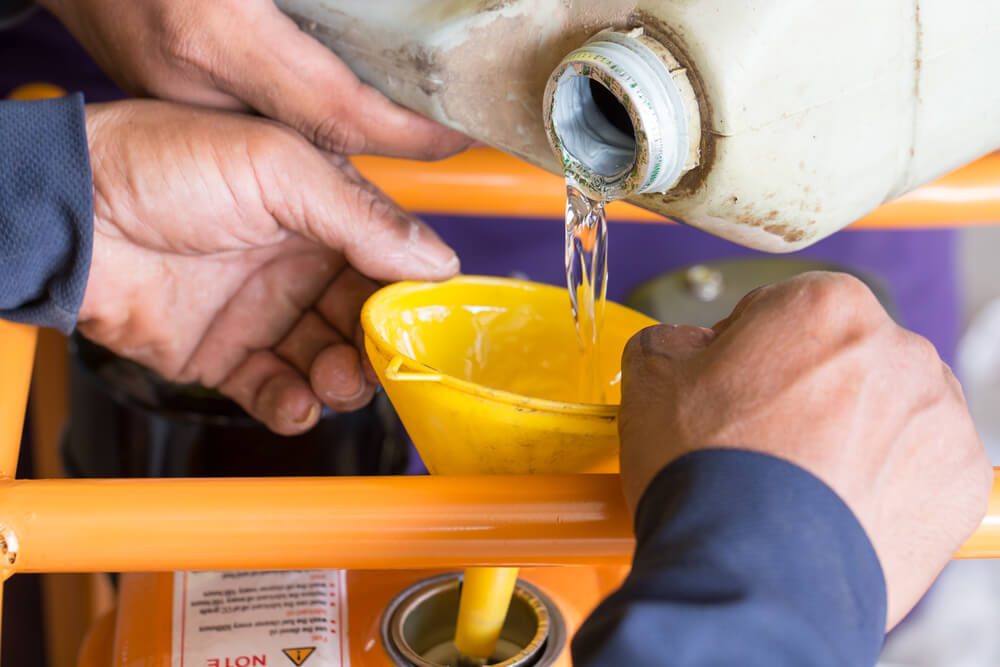

Running your generator on low fuel can do serious damage to the machine. Cheap machines simply run out with no warning, while others provide an automatic shutoff feature that will stop your machine when your natural gas or oil hits a certain low.
However, not all machines have this feature, so keep a close eye on your levels and check them regularly. If you reach low fuel, you may experience a drain in the magnetic field of the electric generator coils, and that can be a costly repair.
Invest in Long Cords
While you shouldn’t use a portable generator more than 100 feet from your appliances, it can be a great relief to invest in long, heavy-duty 12-gauge extension cords. Generators are usually pretty loud. If you’re someone who is disturbed easily by loud noises, you may gain some peace by extending your generator as far from your home as possible during use.
Make sure you have a quality cord, though. A light, flimsy cord can cause a voltage drop and may lead to premature motor burnout.
Related Reading: How Much Gas Does a Generator Use?
Conclusion
Although costly tools, generators are extremely useful in many situations. They are great to have in the home as backup power supplies, and large generators are awesome for industrial use in large businesses or farmlands.
These days, generators allow you to have electricity wherever, and whenever, you need it. Maintain up-to-date knowledge on these products to get the best use out of them.
Want To Learn More About Generators? See Related Topics :